19+ Do Plants Do Glycolysis
Web Glycolysis is a central metabolic pathway that provides energy and generates precursors for the synthesis of primary metabolites to plants. Pay off phase or oxidative phase or exergonic phase or triose phase steps 6-10.
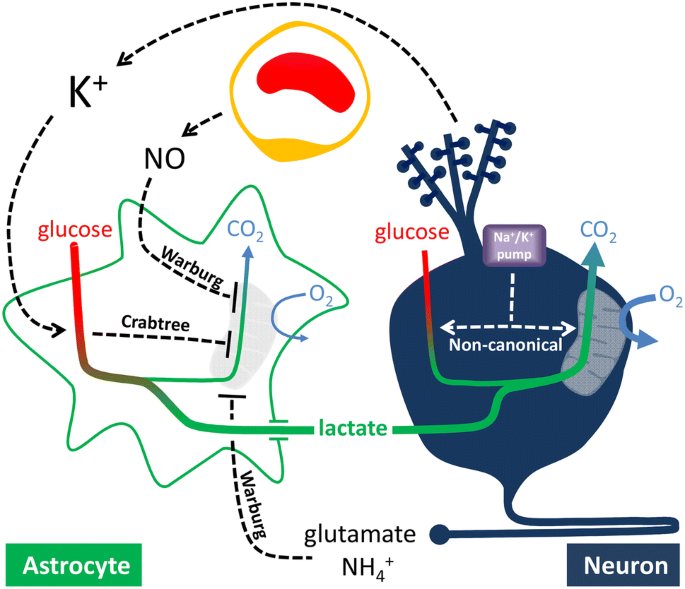
Aerobic Glycolysis In The Brain Warburg And Crabtree Contra Pasteur Springerlink
These enzymes include a pyrophosphate-dependent phosphofructokinase a non-reversible and nonphosphorylating.

. However glycolysis doesnt require oxygen and many anaerobic organismsorganisms that do not use oxygenalso have this pathway. Figure 3 diagrammatically summarizes some of the genes up or downregulated by melatonin that are related to carbohydrate metabolism. First to provide a concise overview of plant gluconeogenesis.
Plant glycolysis exists both in the cytosol and plastid and the parallel reactions are. Web In addition to the clear metabolic intimacy of the organelles of the plant cell mitochondria and chloroplasts have frequently been observed to spatially colocalizea feature that has among. First to provide a concise overview of plant gluconeogenesis.
Web It is divided into two phases. 50 mmolmol at the end of the intervention. Glycolysis is the process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy.
Web Abstract This review discusses the organization and regulation of the glycolytic pathway in plants and compares and contrasts plant and nonplant glycolysis. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate ATP and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NADH. Web Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6 into pyruvate and in most organisms occurs in the liquid part of cells the cytosol.
It produces two molecules of pyruvate ATP NADH and water. Web This review discusses the organization and regulation of the glycolytic pathway in plants and compares and contrasts plant and nonplant glycolysis. Subsequently when malic acid is no longer being released from the vacuole its metabolism in the cytoplasm will reduce its concentration.
Web In organisms that perform cellular respiration glycolysis is the first stage of this process. Web Gluconeogenesis is a key interface between organic acidamino acidlipid and sugar metabolism. Web The cytosolic concentration of PEP is a critical regulator of plant glycolysis and a high concentration of PEP causes a switch to gluconeogenesis.
Web Glycolysis is the first pathway used in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy. Web All organisms from simple bacteria and yeast to complex plants and animals carry out some form of cellular respiration to capture and supply free energy for cellular processes. Web The size of study populations varied between 45 and 291 individuals and the duration of intervention varied from 4 to 24 weeks.
Glucose is phosphorylated into glucose-6-phosphate. Each NADH is equal to 3 ATP so that net gain in glycolysis is 8 ATP. Web In glycolysis two molecules of ATP are consumed during double phosphorylation of glucose to fructose 16 bisphosphate.
Although cellular respiration and photosynthesis evolved as independent processes today they are interdependent. Glycolysis is a process that occurs in the cytoplasm of cells it is common in all kingdoms Plant Animal Fungi Bacteria Protist Archaebacteria Eubacteria. Do Plants Use Glycosis And The Krebs Cycle.
Both plastidial and cytosolic glycolysis must be finely coordinated to provide flexibility to plant development and acclimation to environmental stresses. Two molecules of NADPH2 are formed at the time of oxidation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 13 diphosphoglycerate. The Krebs cycle is a process that helps the body to produce energy.
When the Krebs cycle is not working properly glycosis can occur. Second to emphasise the widespread occurrence of gluconeogenesis and its utilisation in diverse processes. Glycosis is a condition that can occur when the bodys blood sugar levels become too high.
Web Do fungi do glycolysis. The first step in the pathway is the phosphorylation of glucose by hexokinase to form glucose-6-phosphate in an ATP consuming reaction. Web Melatonin clearly over-expressed the transcripts of many enzymes related to photosynthesis starch sucrose glycolysis fermentation the Krebs cycle and other metabolic pathways.
The majority of the studies assessed changes in HbA. Web Biology Biology Article Glycolysis Glycolysis Glycolysis is the metabolic process that converts glucose into pyruvic acid What is Glycolysis. Preparatory phase or endergonic phase or hexose phase steps 1-5.
Web In the present study we demonstrate that glycolysis is necessary for tip cell differentiation and glucose consumption for mitochondrial ATP production for tip cell survival whereas glycolysis as. This process does not require oxygen it is. Gluconeogenesis is a key interface between organic acidamino acidlipid and sugar metabolism.
The first part prepares the six-carbon ring of glucose for cleavage into two three-carbon sugars. Second to emphasise the widespread occurrence of gluconeogenesis and its utilisation in diverse processes. Glycolysis does not require oxygen and only harvests 2 molecules of ATP the universal energy carriercurrency of cells.
The first phase of glycolysis requires energy while the second phase. It was probably one of the earliest metabolic pathways to evolve and is used by nearly all of the organisms on earth. Additionally glycemic markers used for evaluation of improvement in glycemic control varied.
Plant glycolysis exists both in the cytosol and plastid and the parallel reactions are catalyzed by distinct nuclear-encoded isozymes. Web The process of glycolysis occurs within both the cytosol and plastid with reactions in the different compartments catalysed by separate enzyme isoforms. Web Since about 1980 it has become increasingly clear that the cytosolic glycolysis of plants may make use of several enzymes other than the conventional ones found in yeasts muscle tissue and plant plastids.
Glucose enters the glycolysis from sucrose which is the end product of photosynthesis. Web Glycolysis is the first of the main metabolic pathways of cellular respiration to produce energy in the form of ATP. Web Part of Biology Metabolism for survival Revise Video Test 1 2 3 4 5 Glycolysis Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose into two pyruvate molecules.
Glycolysis consists of two parts. The aims of this article are four-fold. The aims of this article are four-fold.
Through two distinct phases the six-carbon ring of glucose is cleaved into two three-carbon sugars of pyruvate through a series of enzymatic reactions.

Cellular Respiration Definition Equation Cycle Process Reactants Products Britannica
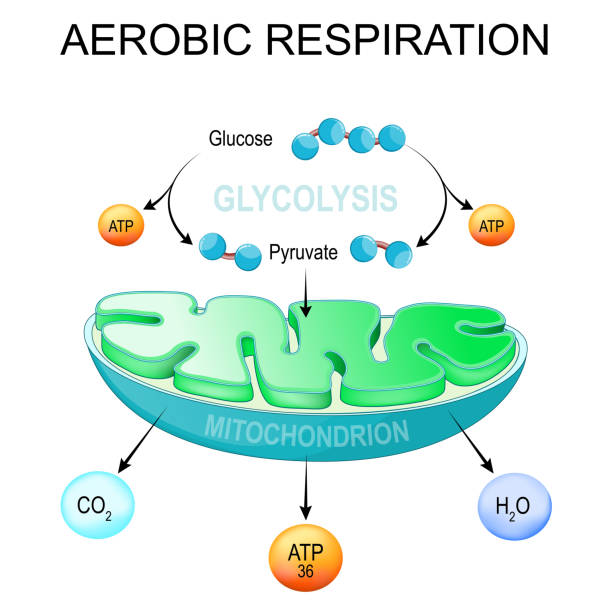
Aerobic Respiration Glycolysis And Atp Synthesis In Mitochondria Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock

3 The Control Of Plant Glycolysis Involves Potent Allosteric Effectors Download Scientific Diagram

What Is The Difference Between Cytosolic And Chloroplastic Glycolysis Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

What Is Glycolysis Cellular Respiration In Plants Biology Class 12 Youtube

Glycolysis Is Important For Optimal Asexual Growth And Formation Of Mature Tissue Cysts By Toxoplasma Gondii Sciencedirect

Glycolysis Cellular Respiration Biology Article Khan Academy
Glycolysis Pathway In Detail How Glucose Is Turned Into Energy Assay Genie
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Cellular-Respiration-58e52b113df78c5162b38dca.jpg)
Learn About The 3 Main Stages Of Cellular Respiration
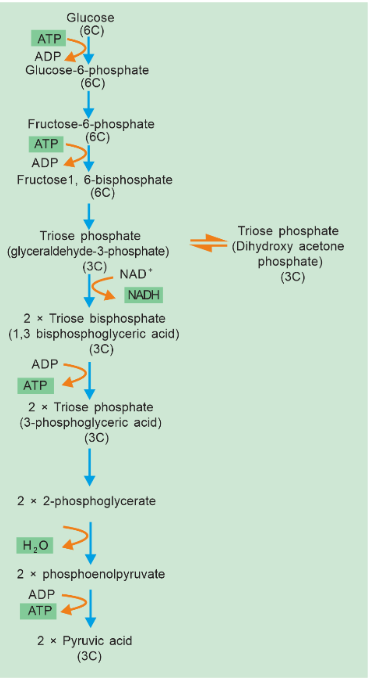
Glycolysis Glycolysis Pathway Glycolysis Cycle Infinity Learn

What Is Glycolysis
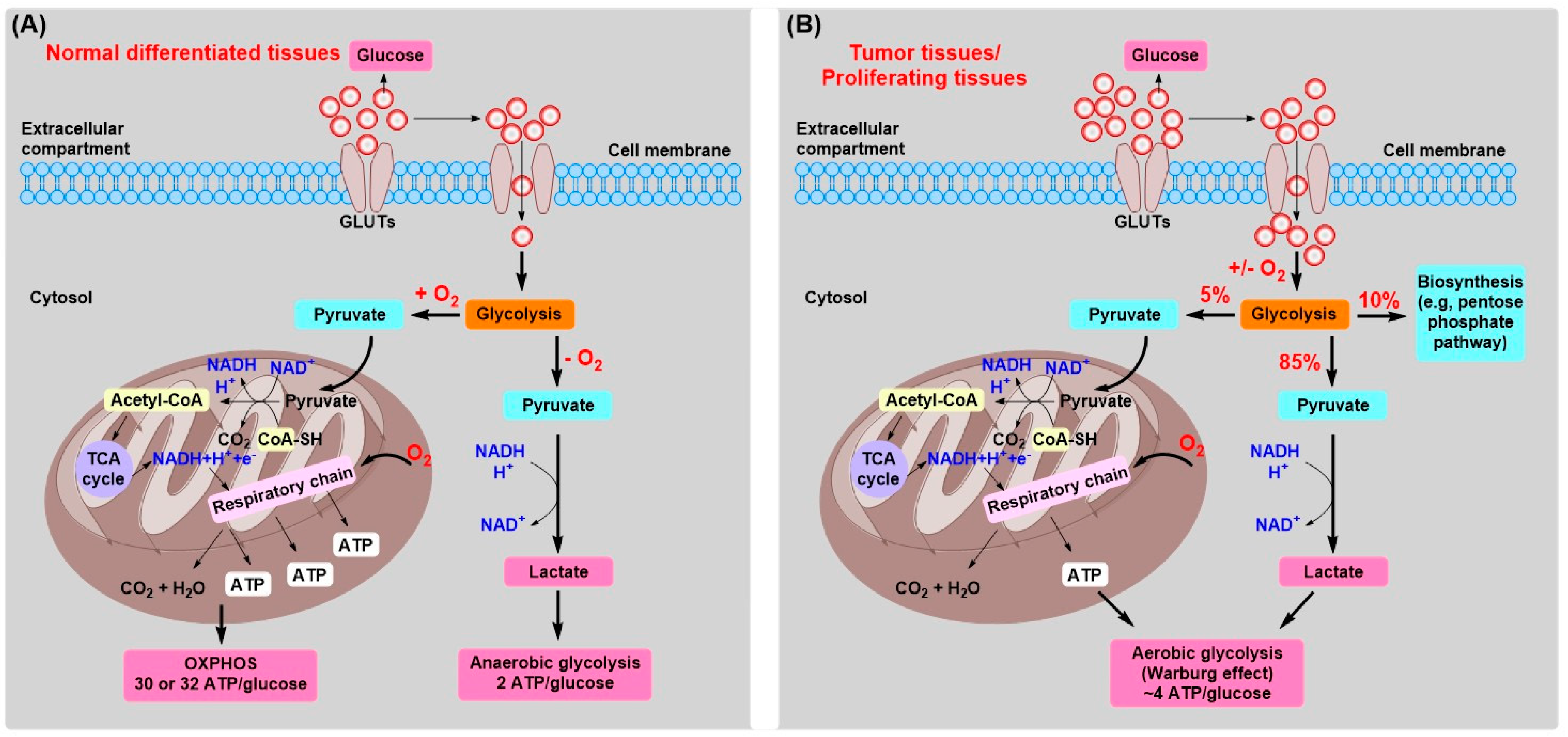
Cancers Free Full Text Tumor Energy Metabolism And Potential Of 3 Bromopyruvate As An Inhibitor Of Aerobic Glycolysis Implications In Tumor Treatment
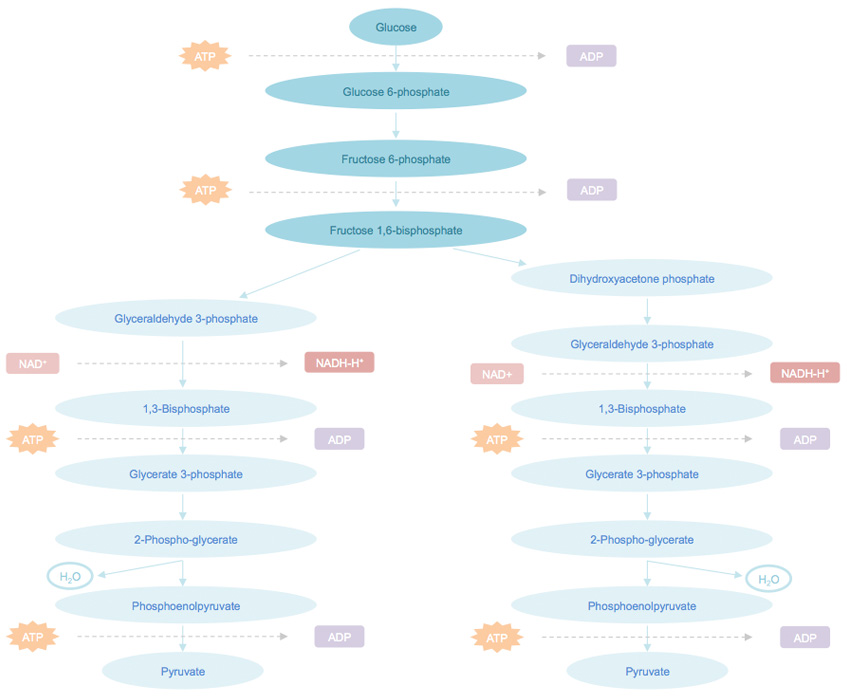
Glycolysis Pathway Analysis Service Creative Proteomics
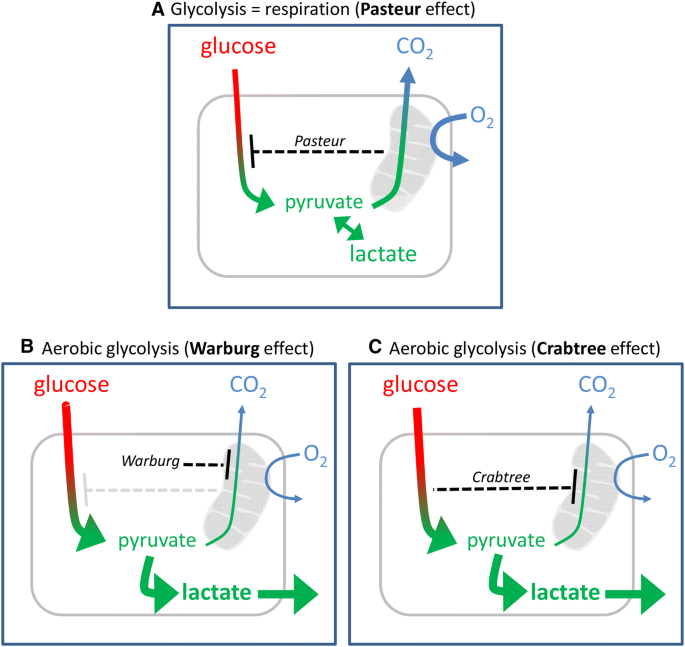
Aerobic Glycolysis In The Brain Warburg And Crabtree Contra Pasteur Springerlink

Aerobic Respiration Glycolysis 12 2 3 Cie A Level Biology Revision Notes 2022 Save My Exams

Mcqs On Glycolysis Biotech Mcq
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Glycolysis-58a468ce3df78c47584cd4d3.jpg)
The 10 Steps Of Glycolysis